Las Vegas, Orlando, Austin lead U.S. with most startup businesses
March 26, 2021
Startups are a significant driver of the U.S. economy. Each year, thousands of entrepreneurs launch new businesses that create jobs and spur innovation and efficiency across the market. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, more than 420,000 startups accounted for 2.2 million new jobs in 2018.
Unfortunately, entrepreneurship in the U.S. has been declining for decades. In the late 1970s, the startup formation rate in the U.S. – defined as the number of new firms in a given year divided by the total number of firms – was nearly 14 percent. Four decades later, the rate was just above 8 percent.
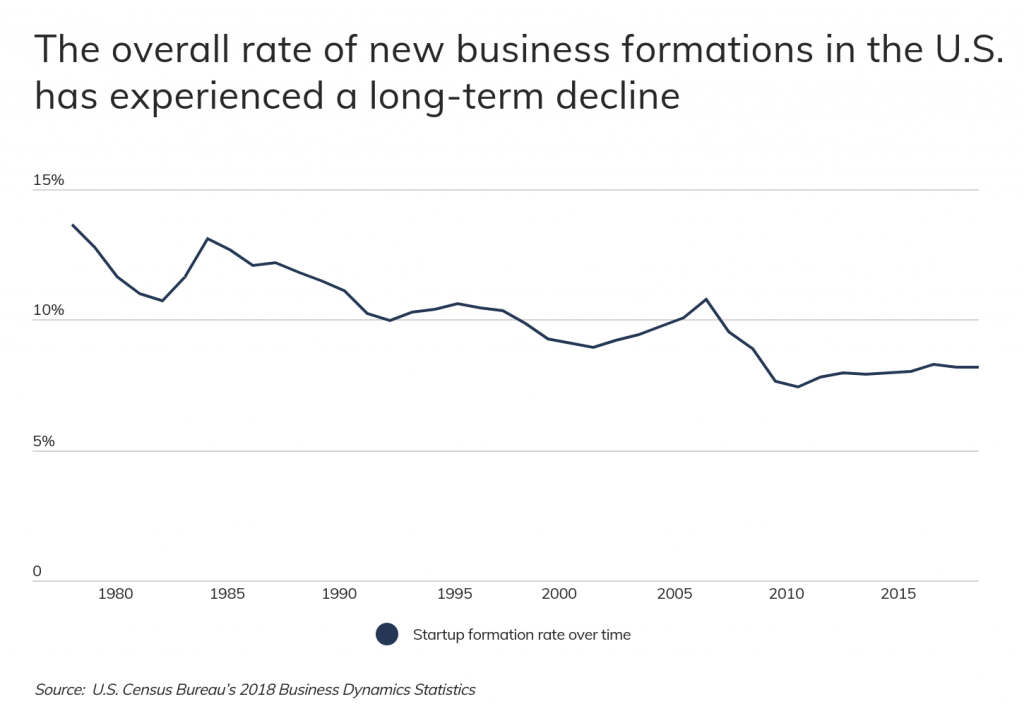
One of the major factors contributing to this trend is firm concentration. In recent decades, many sectors have shown a trend toward consolidation and greater concentration in the market, making large firms even larger and more successful through economies of scale, network effects, and other incumbent advantages.
Economic downturns also tend to slow startup formation, and the Great Recession’s effects on new business creation have proven to be especially stifling over the last decade. Unlike in past recessions, when a dip in startup activity has been followed by a period of growth, the overall startup formation rate fell in the wake of the Great Recession and has more or less remained flat at around 8 percent since. With less economic security due to a long, uncertain recovery, many potential entrepreneurs chose to minimize their risk and forgo new business opportunities. This is especially true of many would-be founders now in their late 20s and 30s, who graduated in a poor job market with large debt burdens.
This past year, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought even more economic hardship, and the unique circumstances of this downturn have created an even more complicated picture. In addition to the typical barriers to entrepreneurship that a recession creates, different industries face divergent fortunes in the era of shutdowns and social distancing. Certain sectors have become even more entrenched in daily life, creating new opportunities for growth in areas like e-commerce, video conferencing, online education, and collaboration tools. On the other hand, COVID-19 is likely to further suppress startup activity in many sectors like accommodation, food services, and retail. In recent years, these fields have experienced stagnant or declining startup formation rates. Today, the prospect of entering these industries will become even more daunting with consumer concerns about health and safety stifling demand and increasing overhead costs.
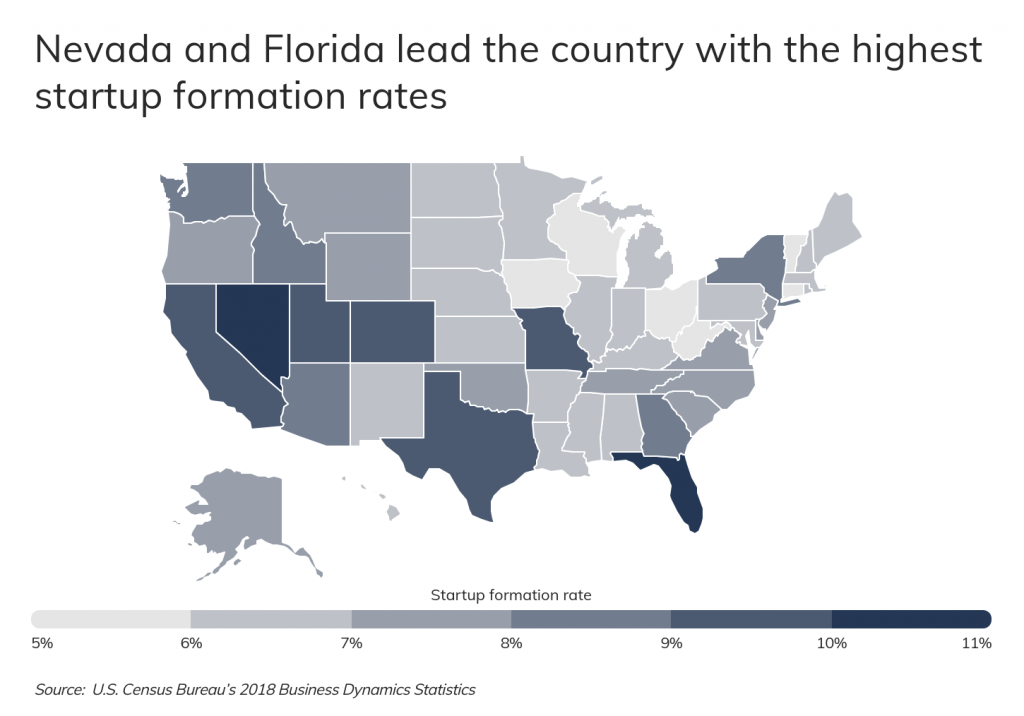
New startup formation is distributed unevenly across geographies as well as industries. Most of the states seeing the highest rates of new business creation are based in the western and southern U.S., led by Nevada (10.39 percent) and Florida (10.16 percent). Many of these states offer some combination of business-friendly policies, low individual and corporate tax rates, relatively low costs to operate, good educational institutions, and population growth that provides both a customer base and a market for labor.
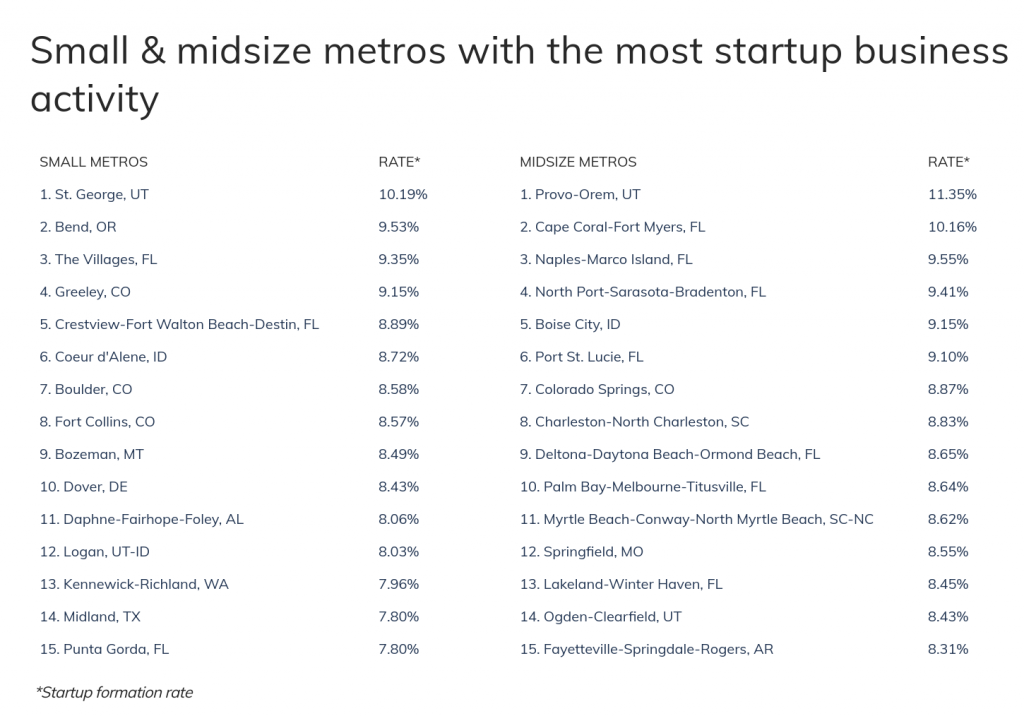
Unsurprisingly, at the metro level, most of the leading hubs for startup formation are found in the states with the highest levels of startup activity. Many locations in the West and South continue to see strong rates of new business creation and associated job growth. To find out which metros are leading the way, researchers at Roofstock calculated the trailing five-year average startup formation—defined as the number of new firms in a given year divided by the total number of firms. The research team also analyzed the impact of startup activity on job growth.
Here are the metropolitan areas with the most startup business activity.
Large Metros With the Most Startup Business Activity

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
15. St. Louis, MO-IL
- Startup formation rate: 9.09%
- Annual startup formations: 4,715
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 19,078
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 12.22%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
14. San Diego-Chula Vista-Carlsbad, CA
- Startup formation rate: 9.28%
- Annual startup formations: 5,599
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 27,338
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 15.13%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
13. Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario, CA
- Startup formation rate: 9.40%
- Annual startup formations: 4,867
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 28,137
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 16.10%
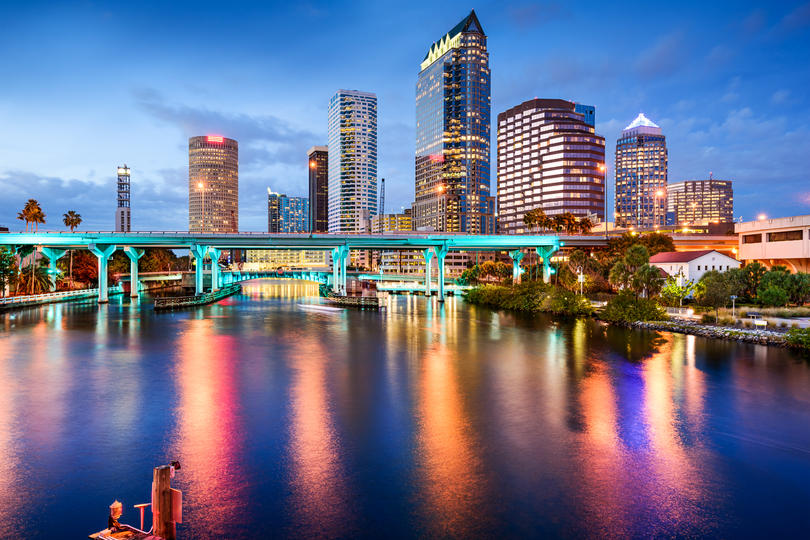

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
12. Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, FL
- Startup formation rate: 9.47%
- Annual startup formations: 5,174
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 25,792
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 12.31%
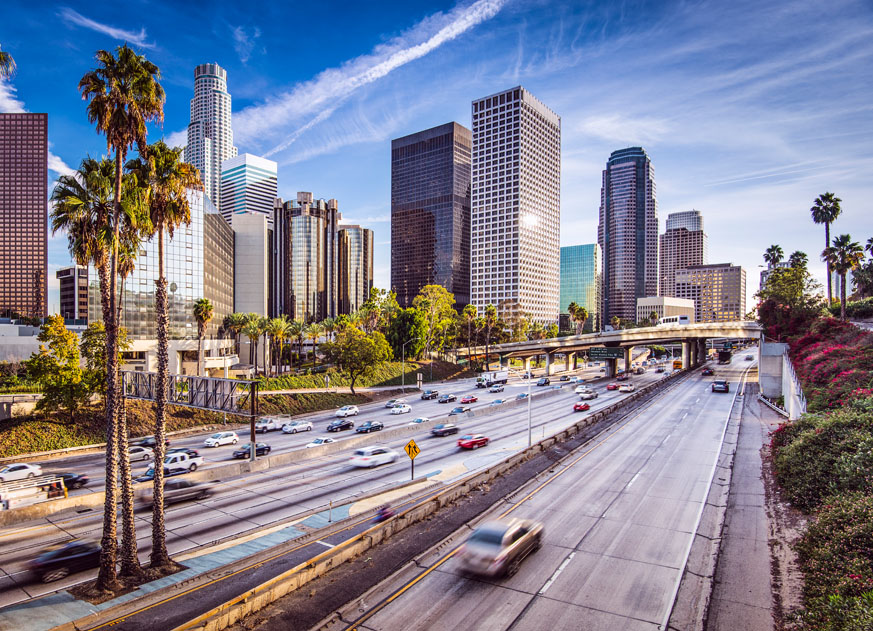

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
11. Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA
- Startup formation rate: 9.47%
- Annual startup formations: 24,718
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 144,716
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 18.05%
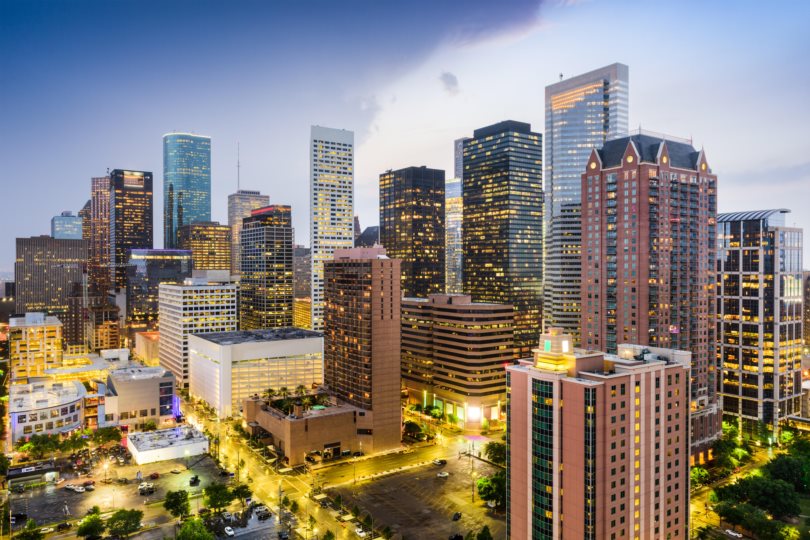

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
10. Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land, TX
- Startup formation rate: 9.48%
- Annual startup formations: 9,214
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 55,475
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 14.44%
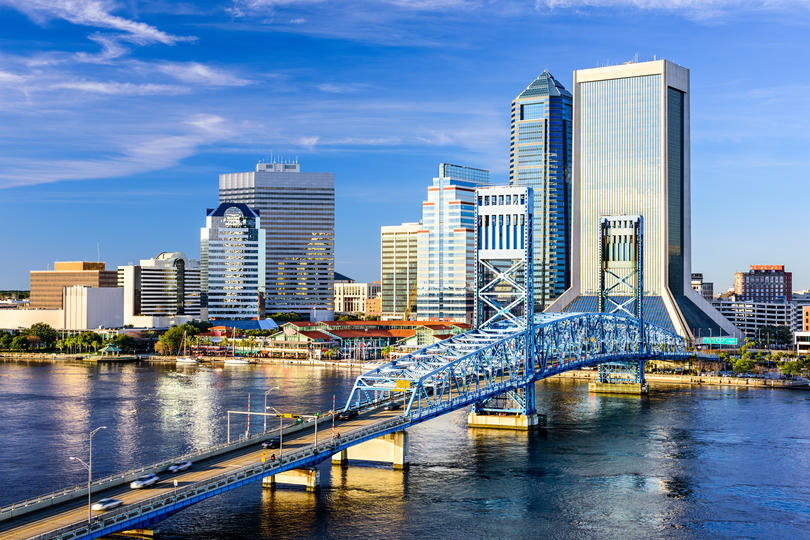

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
9. Jacksonville, FL
- Startup formation rate: 9.50%
- Annual startup formations: 2,474
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 11,796
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 14.41%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
8. Atlanta-Sandy Springs-Alpharetta, GA
- Startup formation rate: 9.52%
- Annual startup formations: 9,140
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 48,582
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 14.14%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
7. Phoenix-Mesa-Chandler, AZ
- Startup formation rate: 9.63%
- Annual startup formations: 6,108
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 37,785
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 14.02%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
6. Denver-Aurora-Lakewood, CO
- Startup formation rate: 9.64%
- Annual startup formations: 5,590
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 28,485
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 14.69%

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
5. Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington, TX
- Startup formation rate: 9.82%
- Annual startup formations: 10,731
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 69,696
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 15.11%
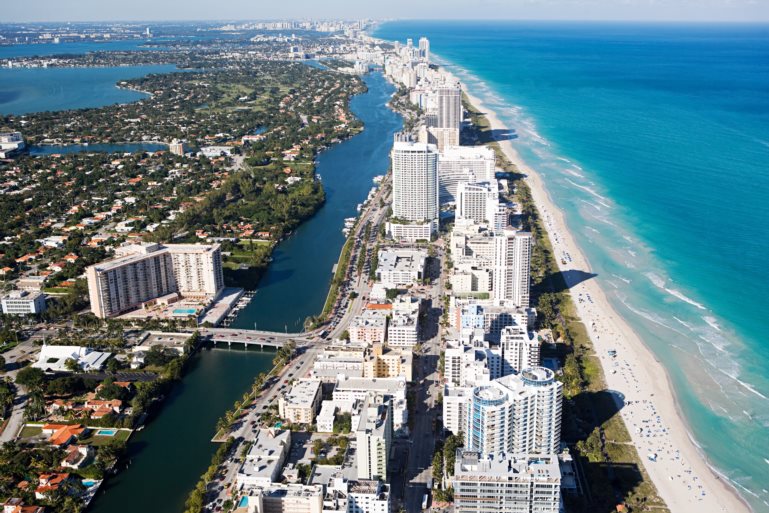

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
4. Miami-Fort Lauderdale-Pompano Beach, FL
- Startup formation rate: 10.46%
- Annual startup formations: 14,894
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 69,769
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 18.57%
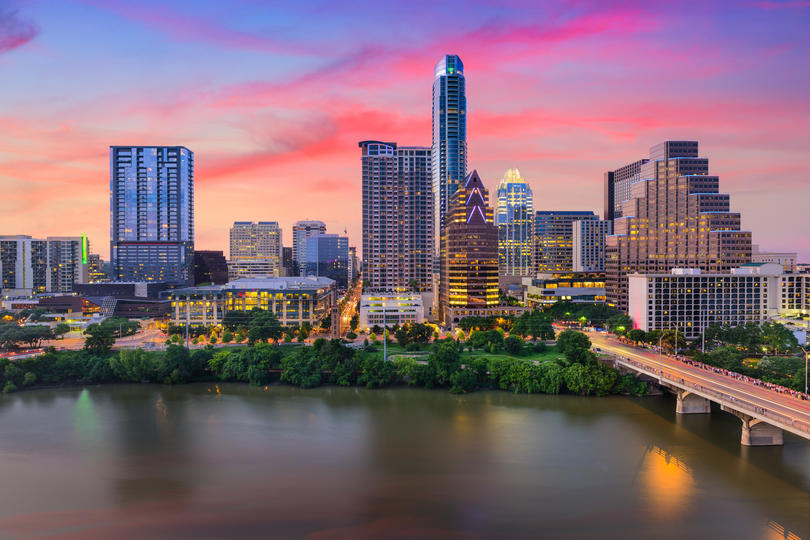

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
3. Austin-Round Rock-Georgetown, TX
- Startup formation rate: 10.61%
- Annual startup formations: 3,858
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 21,357
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 16.49%
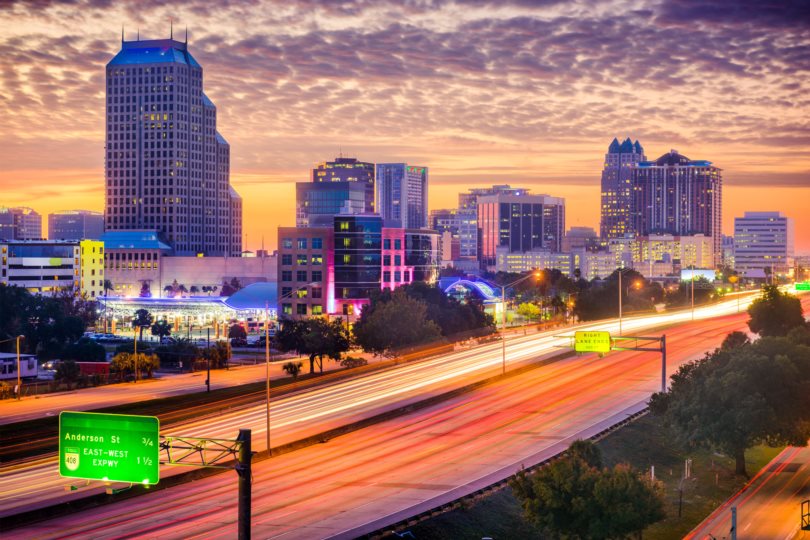

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
2. Orlando-Kissimmee-Sanford, FL
- Startup formation rate: 10.95%
- Annual startup formations: 4,861
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 25,533
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 16.68%
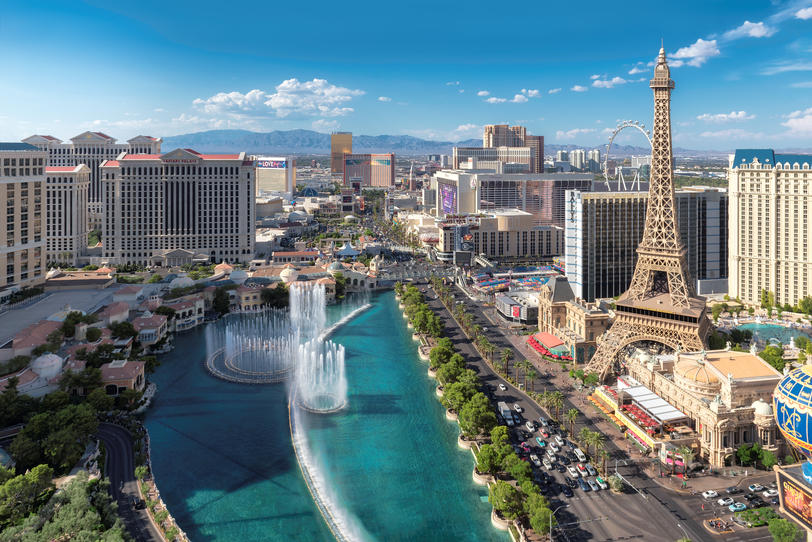

Photo Credit: Alamy Stock Photo
1. Las Vegas-Henderson-Paradise, NV
- Startup formation rate: 11.44%
- Annual startup formations: 3,467
- Annual new jobs created by startups: 21,074
- Jobs created by startups as a percentage of all new jobs: 17.82%
Detailed Findings and Methodology
The data used in this analysis is from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2018 Business Dynamics Statistics, which includes all U.S. businesses with paid employees. To identify locations with the most startups, researchers calculated the trailing five-year (2014–2018) average startup formation rate—defined as the number of new firms in a given year divided by the total number of firms. Researchers also calculated the average annual number (and proportion) of new jobs created by startup firms between 2014 and 2018. To improve relevance, only metropolitan areas with at least 100,000 residents were included. Additionally, metros were grouped into cohorts based on population size: small (100,000–349,999), midsize (350,000–999,999), and large (1,000,000 or more).















